Introduction To The Nine Planetary Boundaries
Planetary Boundaries refer to a framework for understanding and addressing the environmental challenges facing our planet. The concept was first introduced in 2009 by a group of scientists led by Johan Rockström and is based on the idea that there are certain “boundaries” or limits within which humanity must operate to maintain a stable and healthy Earth system.
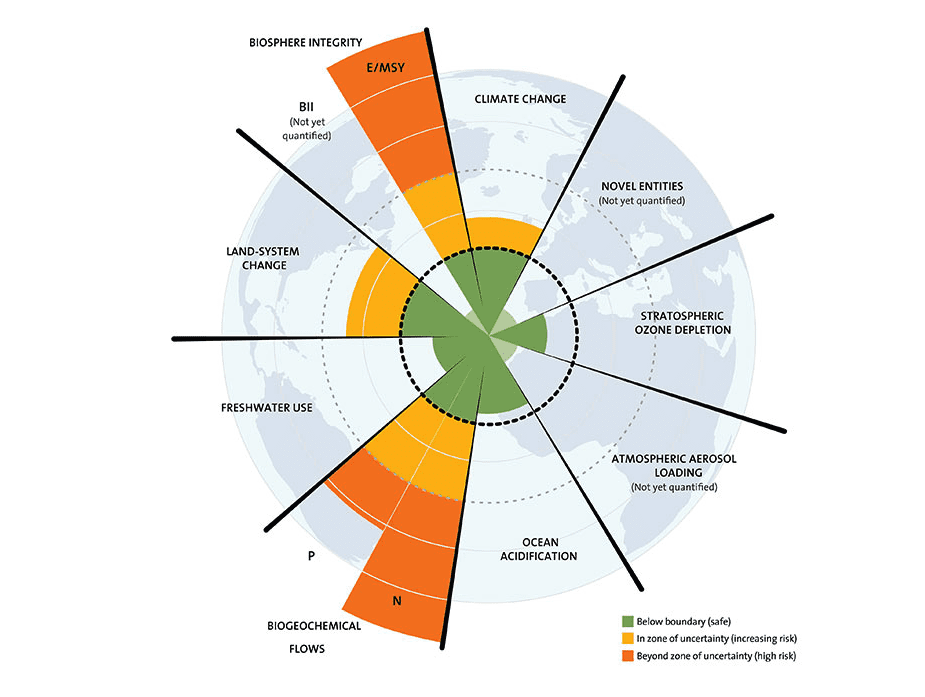
The concept of planetary boundaries identifies nine key Earth system processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the planet, including:
- Climate change: The concentration of atmospheric greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, that contribute to global warming.
- Biodiversity loss: The rate of extinction of plant and animal species.
- Land use change: The conversion of natural habitats into human-dominated landscapes, such as cities or agricultural fields.
- Freshwater use: The rate at which water is extracted from rivers, lakes, and groundwater reserves.
- Ocean acidification: The increase in acidity of the oceans as a result of the absorption of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- Ozone depletion: The reduction in the thickness of the protective ozone layer in the Earth’s stratosphere.
- Atmospheric aerosol loading: The concentration of tiny particles in the atmosphere that can affect climate and human health.
- Chemical pollution: The release of synthetic chemicals into the environment that can harm living organisms.
- Nitrogen and phosphorus cycles: The excessive use of fertilizers and other chemicals that can lead to the degradation of ecosystems.
The planetary boundaries concept emphasises that crossing one or more of these boundaries could result in abrupt and irreversible environmental changes that would threaten the long-term sustainability of human societies. The framework serves as a useful guide for policymakers and individuals seeking to achieve a sustainable future for our planet by identifying key areas where action is needed to maintain a stable and healthy Earth system.